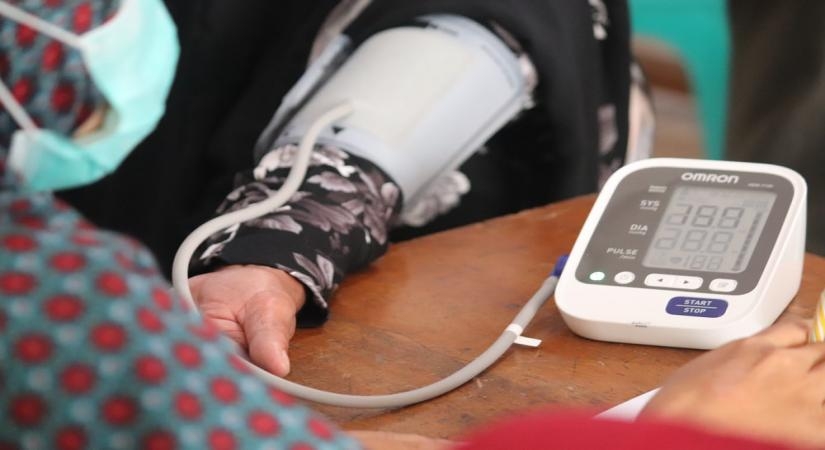
Low potassium symptoms can lead to symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, heart palpitations, and high blood pressure, among others…reports Asian Lite News
Beta blockers, widely used medications for managing high blood pressure and heart conditions, are not commonly associated with lowering potassium levels, according to medical experts. Concerns arose following an alert from the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) earlier this week, warning of potential risks of hypokalemia—a condition characterized by low potassium levels—linked to beta blocker usage.
Beta blockers, such as Metoprolol, Propranolol, and Atenolol, are prescribed for treating hypertension and irregular heartbeats. They function by inhibiting adrenaline’s effects, leading to relaxed and dilated blood vessels and a reduced heart rate.
The IPC, operating under the Union Health Ministry, cautioned about the potential for hypokalemia in patients using beta blockers. Symptoms of low potassium include muscle weakness, fatigue, heart palpitations, and elevated blood pressure.
Dr. Rajeev Jayadevan, Chairman of the Kerala State IMA Research Cell, reassured the public, stating, “Beta blockers are not typically known to cause hypokalemia.” He emphasized that hypokalemia is more likely when diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide and frusemide, are used concurrently with beta blockers. Diuretics aid in reducing fluid buildup and can lower potassium levels, increasing the risk when combined with other medications.
“People taking only a beta blocker are extremely unlikely to develop hypokalemia,” Dr. Jayadevan confirmed.
Dr. Ashwani Mehta, a prominent cardiologist, criticized the alert, stating it has incited unnecessary fear among patients. “Beta blockers have been safely used for 25 to 30 years in our country. Significant hypokalemia is rare unless severe comorbid conditions are present,” Dr. Mehta explained.
He assured patients that beta blockers remain well-tolerated, adding, “This alert has caused undue panic, which is unwarranted.”
Healthcare professionals are advised to monitor patients for potential adverse reactions carefully. However, experts maintain that beta blockers are generally safe and effective, with low risk of inducing hypokalemia in the absence of diuretics or other contributing factors.